
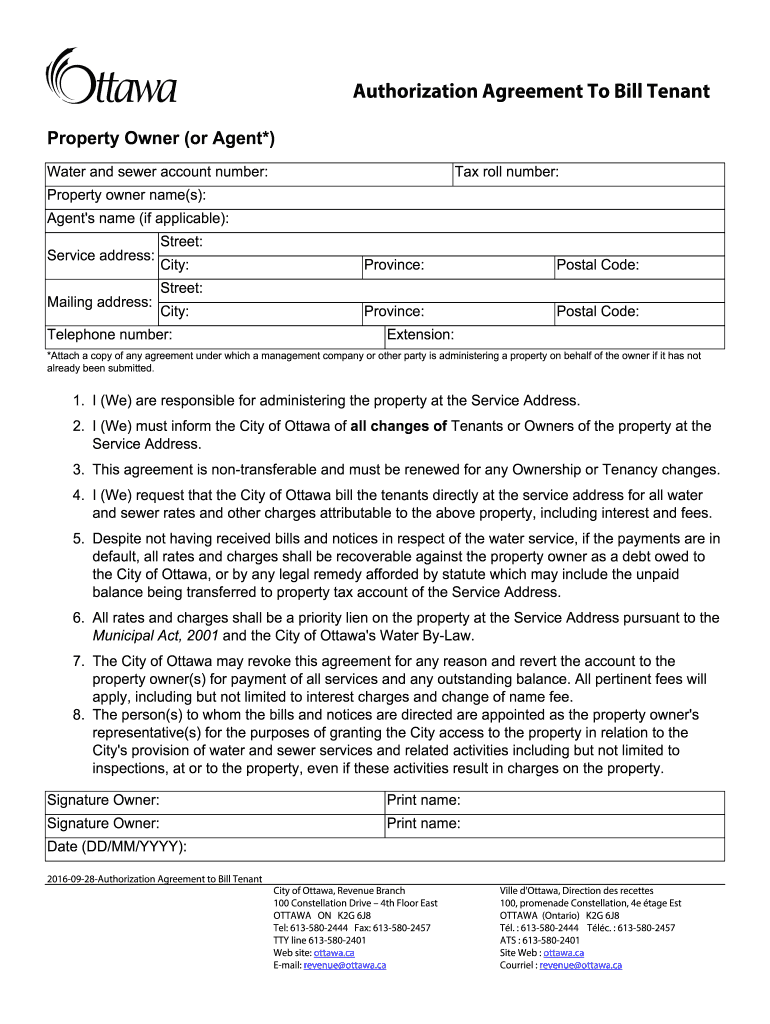
Taxable income includes income from employment or self-employment, pensions, rental properties, royalties, financial investments and numerous government benefits some of these benefits relate to Government of Canada COVID-19–related payments. In Canada, various sources of domestic and foreign income are taxed, although individuals can claim a tax credit for taxes paid in foreign countries. The income thresholds for tax brackets, as well as certain other amounts within the personal income tax system, are indexed to inflation every year. 15.0% on the first $49,020.00 of taxable income.įederal personal income tax rates for the 2021 taxation year are:
Source: Figure prepared by the Library of Parliament using data obtained from Canada Revenue Agency, Tax packages for all years. Note: The personal income tax brackets and rates have been unchanged since 2016. Figure 3 – Personal Income Tax Brackets and Rates in Canada, 1987–2021 Figure 3 shows changes in the number of personal income tax brackets and their respective rates since 1987. Over time, the number of federal personal income tax brackets, each bracket’s income thresholds and the tax rates applicable to those brackets have changed. Source: Figure prepared by Nathalie Pothier, Library of Parliament using data obtained from Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), “ Revenue Statistics – OECD Countries: Comparative Tables ,” Database, accessed on 30 March 2021. Note: “Other taxes and contributions” includes corporate income taxes, social security contributions, payroll and workforce taxes, property taxes, taxes on goods and services, and other taxes. Figure 2 – Revenue from Personal Income Tax, and Other Taxes and Contributions, as a Percentage of Gross Domestic Product, All Levels of Government, Selected Countries, 2018 Sources: Figure prepared by Nathalie Pothier, Library of Parliament using data obtained from: Statistics Canada, “ Table 10-10-0015-01: Statement of government operations and balance sheet, government finance statistics (x1,000,000) ,” Database, accessed on 16 February 2021 and Receiver General for Canada, Public Accounts of Canada 2020, Volume 1, 2020.Īs shown in Figure 2, as a percentage of gross domestic product, Canada’s personal income tax revenue in 2018 was higher than the average for Organisation for Economic Co‑operation and Development (OECD) countries and the highest among the Group of Seven, or G7, countries. “Other taxes and revenue” are non-resident income taxes, revenue from federal enterprise Crown corporations and similar entities, net foreign exchange revenue and revenue from other programs. “Consumption taxes” are the Goods and Services Tax, the Harmonized Sales Tax, energy taxes, customs import duties, other excise taxes and duties, and fuel charges. For the purposes of this figure, QPP contributions are combined with contributions to the CPP, giving rise to the term “federal.” The QPP operates exclusively in Quebec, with the CPP operating in the rest of Canada. Notes: “Social security contributions” are Canada Pension Plan and Quebec Pension Plan (CPP and QPP) contributions, and Employment Insurance premiums. Figure 1 – Federal Tax Revenue and Social Security Contributions, 2019–2020 ($ billions) Revenueįigure 1 shows that, in 2019–2020, personal income tax revenue totalled $167.6 billion and represented 41.3% of total federal tax revenue and social security contributions. Other HillNotes discuss corporate income taxes, consumption taxes and social security contributions.

This HillNote provides information about the revenue, rates and rationale relating to federal personal income taxes in Canada. In Canada, sources of funds that help to finance federal initiatives include personal income taxes, corporate income taxes, consumption taxes and social security contributions. The first of these activities – taxation – can take several forms. Governments finance the goods and services that they provide in various ways, including through taxing, investing and borrowing activities. Personal Income Taxes in Canada: Revenue, Rates and Rationaleīy loprespub on OctoReading Time: 6 minutes Home › Economics and Finance › Personal Income Taxes in Canada: Revenue, Rates and Rationale


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
